In this blog tutorial, I will demonstrate how to set up a GraphQL server in Deno with gql, a framework-agnostic GraphQL middleware.
# GraphQL Schema
We’ll start with declaring a schema using type definitions and resolvers using graphql_tag and graphql_tools Deno modules, similar to how you do it with Apollo Server or GraphQL Yoga:
import { gql } from 'https://deno.land/x/graphql_tag/mod.ts'
import { makeExecutableSchema } from 'npm:@graphql-tools/schema@10.0.3'
const typeDefs = gql`
type Query {
hello: String
}
`
const resolvers = {
Query: {
hello: () => `Hello World!`,
},
}
const schema = makeExecutableSchema({ resolvers, typeDefs })Now we have an executable schema that can be passed to a GraphQL server.
# Server setup
In order to setup gql you just need to pass a req object to it so it can read request body and properties.
import { GraphQLHTTP } from 'https://deno.land/x/gql/mod.ts'
// schema code
Deno.serve({
port: 3000,
onListen({ hostname, port }) {
console.log(`☁ Started on http://${hostname}:${port}`)
},
}, async (req) => {
const { pathname } = new URL(req.url)
return pathname === '/graphql'
? await GraphQLHTTP<Request>({
schema,
graphiql: true,
})(req)
: new Response('Not Found', { status: 404 })
})Now run the server with these permissions (for reading body and using network):
deno run --allow-net --allow-read server.ts# GraphQL Playground
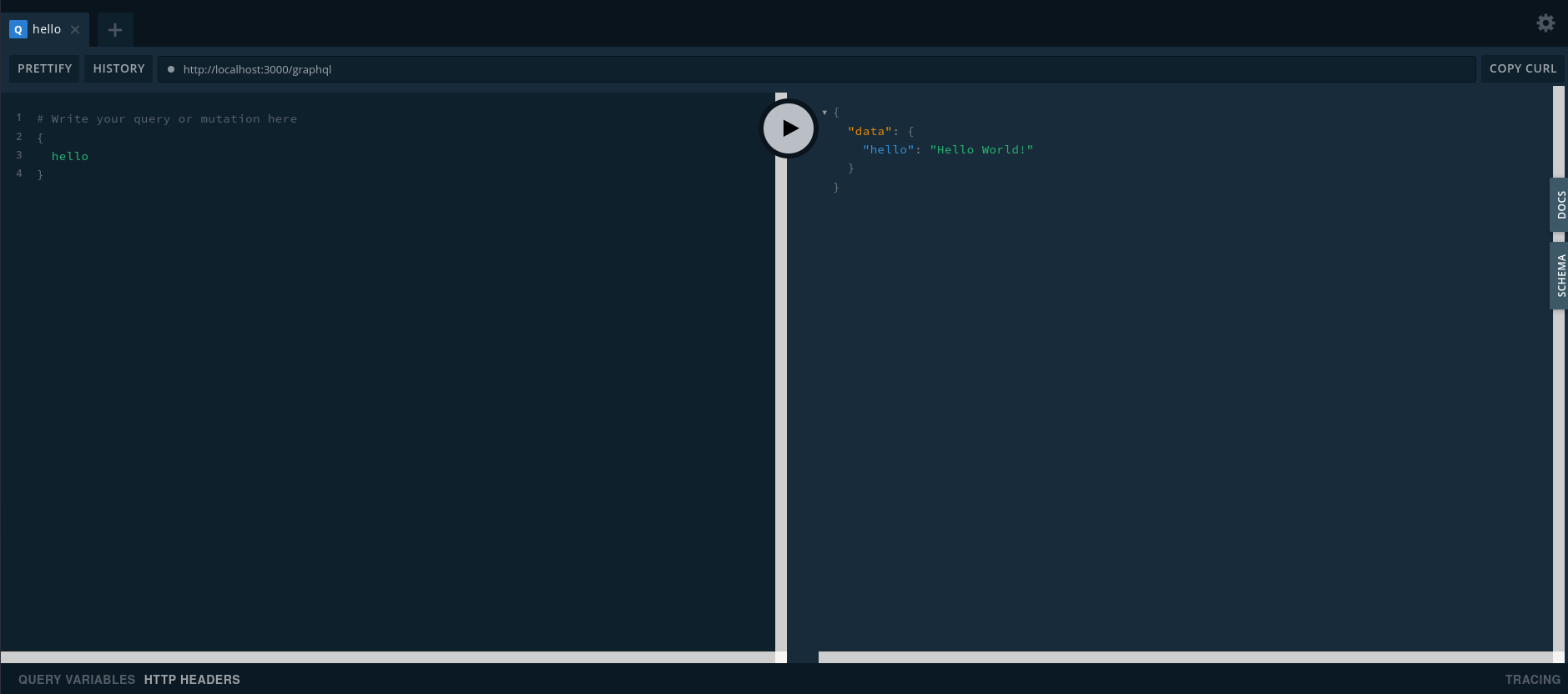
With server set up and graphiql enabled, the GraphQL Playground will launch as well.
Open your browser on http://localhost:3000 and you will see this:
# Conclusion
This is how you can set up a simple GraphQL server for Deno without any backend frameworks. There are a few examples of using gql with other frameworks, check them out.
